Dear Prakhar,
In nonlinear analysis things are not so easy as in linear one, mesh quality is critical to arrive to a convergence solution, also you need to read NX NASTRAN manuals to understabd the nonlinear parameters, I strongly suggest to contact sur SIEMENS VAR RESELLER to ask for NX AdvSim CAE training, this forum only can provide some tips & tricks, but with alimited path.
To start with, for nonlinear analysis you may define the simplest model as possible: for instance, I note the material has defined a stress-strain relationship, then the solver will account for material nonlinearities when running the analysis. Change the material to not consider any material nonlinerarity in the first analysis. If the problem solve with success, that revise results and add material nonlinear model if required and repeat the analysis.
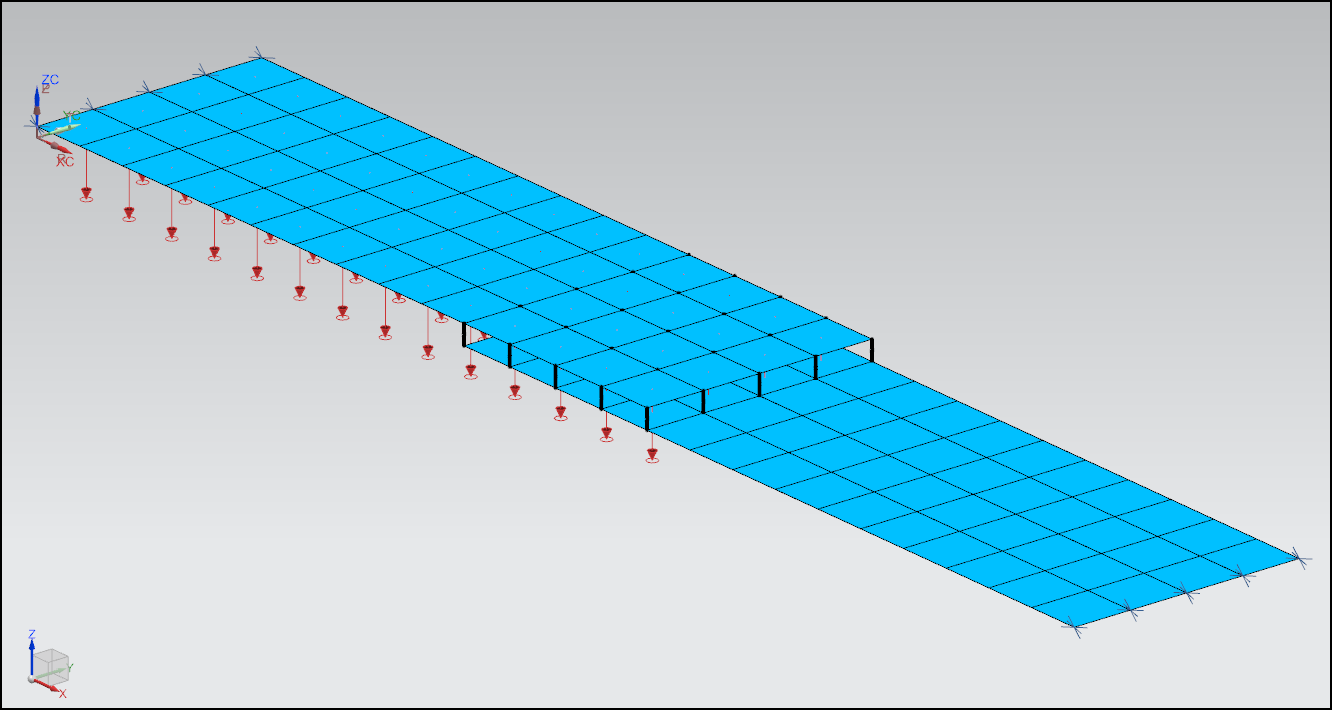
Also, revising the mesh I note that RBE3 RIGID elements are included in the FEM model!. In fact, "surface-Contact-mesh" based in node-yo-node CGAP elements is tricky in NX ADVSIM, if the two end nodes of the CGAP elements are not exactly coincident and alligned then NX AdvSim will create in one end a spider based in RBE3 elements to "solve" the problem. If I open the model in FEMAP you can see the spiders used based in RBE3 elements (in white color).

This is a problem because rigid elements for nonlinear analysis are of not good for the NX NASTRAN solver, is not reconmended at all, then in the future make sure that both nodes of the CGAP element are perfectly aligned, ie, the mesh in top and bottom plates in contact should be exactly coincident to avoid the creation of rigid elements. Simply make an imprint of the top edges in the bottom surface and you are done, this way the mesh in both plates will be identical. According the NX NASTRAN BASIC NONLINEAR ANALYSIS GUIDE "Rigid body elements (RBEi, RBAR, RROD entries, etc.) do not rotate in geometric nonlinear analysis", then its use should be avoided as much as possible.
Also, one limitation for CGAP node-to-node in nonlinear analysis is that one of the contact surfaces should not rotate by a large angle because the gap element orientation is not updated for large rotations. If large rotation exsit, then the ADVANCED NONLINEAR MODULE is recomended where the full "surface-to-surface contact" is supported, not need to use 1-D node-to-node contact, OK?.
And finally, the CGAP properties (the PGAP card) at the beginning should be as simply as possible, avoid the use of friction, this will add complexity to the convergence, start without friction.
Regarding nonlinear parameters (NLPARM card) start with 50 increments using the stiffness update strategy = ITER method and Number of iterations before the stiffness update = 1.
_
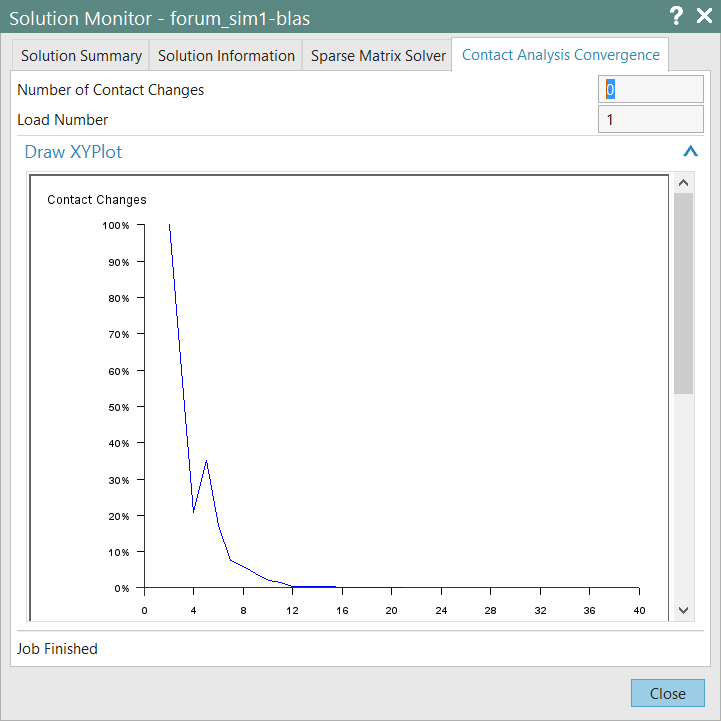
Run the nonlinear static analysis (SOL106) and the convergence will be reached in 184 iterations:
Plot the displacements and stress results AT EVERY STEP and compare with the linear static analysis (SOL101), now you will understad why linear static results are meaningless when geometric nonlinear large displacements effects are involved. Here you are attached the NX NASTRAN *.dat input file.
Best regards,
Blas.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Blas Molero Hidalgo
Ingeniero Industrial
Director
IBERISA
48004 BILBAO (SPAIN)
WEB:
Blog de FEMAP & NX Nastran: