Navigation
Install the app
How to install the app on iOS
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
More options
Style variation
-
Congratulations JStephen on being selected by the Eng-Tips community for having the most helpful posts in the forums last week. Way to Go!
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
UHV/EHV Cables in aerial rack distance to Coke/Blast Furnace Gas
- Thread starter Jpascp
- Start date
bacon4life
Electrical
Is that a gas pipeline feeding the blast furnace? Or exhaust gases from the blast furnace? Would the area be explosive (i.e. classified)?
- Moderator
- #3
Are the cables passing through a hazardous area as classified by the applicable code?
The cables may or may not need to be rated for hazardous locations.
Are the cables passing through an area of high ambient temperatures?
The cables may need to be de-rated, or a higher temperature rated cable may be needed.
At lower voltages, Mineral Insulated cables may meet both hazardous location requirements and high ambient temperature requirements, with suitable de-rating.
The cables may or may not need to be rated for hazardous locations.
Are the cables passing through an area of high ambient temperatures?
The cables may need to be de-rated, or a higher temperature rated cable may be needed.
At lower voltages, Mineral Insulated cables may meet both hazardous location requirements and high ambient temperature requirements, with suitable de-rating.
- Thread starter
- #4
Energy gases (COG, BGF and BOFG) are mixed, and the result is called BLG (“blandgas”). This gas will be fed a CHPP.Is that a gas pipeline feeding the blast furnace? Or exhaust gases from the blast furnace? Would the area be explosive (i.e. classified)?
Regarding ATEX maybe in some areas where are located some valves/instruments in that pipes.
Main goal is to calculate the minimum distance between UHV/EHV cables and that pipe.
- Thread starter
- #5
I believe the pipe with energy gases (COG, BGF and BOFG) could be classified and we are aware to leave a minimum distance to it. Apart of ATEX could be another issue related with EMC. Yes the pipe has high temperatures (I do not know the value).Are the cables passing through a hazardous area as classified by the applicable code?
The cables may or may not need to be rated for hazardous locations.
Are the cables passing through an area of high ambient temperatures?
The cables may need to be de-rated, or a higher temperature rated cable may be needed.
At lower voltages, Mineral Insulated cables may meet both hazardous location requirements and high ambient temperature requirements, with suitable de-rating.
We are talking UHV/EHV cables = 400 kV and 230 kV
NEC art.503.10 for wiring above coke field.
NESC Rule 234. Clearance of wires, conductors, cables, and equipment from buildings, bridges, rail cars, swimming pools, and other installations
However Jpascp said:
Is there any standard that refers to the minimum distance between UHV/EHV Cables and Coke/Blast Furnace Gas?
The Code of Practice for Avoiding Danger from Overhead Electricity Lines- presents a minimum
horizontal distance from the line to the site [no-tip zone] to protect the personnel, equipment, and material in the vicinity.
NESC Rule 234. Clearance of wires, conductors, cables, and equipment from buildings, bridges, rail cars, swimming pools, and other installations
However Jpascp said:
Is there any standard that refers to the minimum distance between UHV/EHV Cables and Coke/Blast Furnace Gas?
The Code of Practice for Avoiding Danger from Overhead Electricity Lines- presents a minimum
horizontal distance from the line to the site [no-tip zone] to protect the personnel, equipment, and material in the vicinity.
Usually, the coke used in a Blast Furnace is conveyed as solid particles of 100-200 grams from the storage to the highest level of the blast furnace and introduced from here together with the ore and other materials through open conveyors.
If the cables are insulated, shielded, and grounded, no distance is required from the power cable tray to the coke conveyor. Maybe if the coke catches fire, the intersection place has to be protected by fire protection.
See NFPA 850 paragraph 7.4.4 coal conveyors, for instance.
In my opinion, paragraph 7.4.5 it is also interesting [Coal Conveying and Handling Structures].
If the cables are insulated, shielded, and grounded, no distance is required from the power cable tray to the coke conveyor. Maybe if the coke catches fire, the intersection place has to be protected by fire protection.
See NFPA 850 paragraph 7.4.4 coal conveyors, for instance.
In my opinion, paragraph 7.4.5 it is also interesting [Coal Conveying and Handling Structures].
- Thread starter
- #8
Thanks however I mentioned pipe gas and not come conveyor.Usually, the coke used in a Blast Furnace is conveyed as solid particles of 100-200 grams from the storage to the highest level of the blast furnace and introduced from here together with the ore and other materials through open conveyors.
If the cables are insulated, shielded, and grounded, no distance is required from the power cable tray to the coke conveyor. Maybe if the coke catches fire, the intersection place has to be protected by fire protection.
See NFPA 850 paragraph 7.4.4 coal conveyors, for instance.
In my opinion, paragraph 7.4.5 it is also interesting [Coal Conveying and Handling Structures].
The gas resulting from the melting process may be conveyed to another place to be used. For a power station gas turbine [fuel], for instance.
No power cable should be above the gas conduit.
On the Blast Furnace Complex, where I was, 110 kV cables ran underground.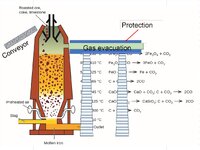
See NFPA 850 7.2 Fuel Handling — Gas[ and NEC art.501]
No power cable should be above the gas conduit.
On the Blast Furnace Complex, where I was, 110 kV cables ran underground.

See NFPA 850 7.2 Fuel Handling — Gas[ and NEC art.501]
You said: The main goal is to calculate the minimum distance between UHV/EHV cables and that pipe.
If the transmission line goes parallel with the pipeline, induced voltages and currents are present in the pipe.

There is a book[EL-904-V1+V2] as a result of the collaboration of EPRI [Electric Power Research Institute ] and Pipeline Research Committee [PRC] for calculating the electromagnetic influence in a pipe.
If the transmission line goes parallel with the pipeline, induced voltages and currents are present in the pipe.

There is a book[EL-904-V1+V2] as a result of the collaboration of EPRI [Electric Power Research Institute ] and Pipeline Research Committee [PRC] for calculating the electromagnetic influence in a pipe.
Similar threads
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 3K
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 818
- Locked
- Question
- Replies
- 0
- Views
- 2K
- Locked
- Question
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 4K
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 4K
